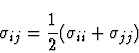To describe a molecule or molecular system, you need to provide a description
of the location of the atoms (the atom coordinates)
and how they are connected together (the molecule topology).
Furthermore, you must also provide force constants
for the interactions between atoms which are bonded together,
and for interactions between atoms which are not bonded.
The former interactions are referred to as the bonded interactions,
while the Coulomb and van der Waals interactions are referred to
as the non-bonded interactions.
Van der Waals ![]() and
and ![]() parameters must be
specified for interactions between all different types of `like' atoms,
and, from these, the parameters for interactions between `different' atoms
are derived from the `like' atom parameters using
the arithmetic average for sigma and the geometric mean for epsilon:
parameters must be
specified for interactions between all different types of `like' atoms,
and, from these, the parameters for interactions between `different' atoms
are derived from the `like' atom parameters using
the arithmetic average for sigma and the geometric mean for epsilon: