Table i compares the accuracy of force calculations achieved
by the approximation schemes SAMM, FAMUSAMM/DC-1d
and FAMUSAMM/linear, respectively.
As accuracy measures the table displays the time averages
![]() and standard deviations
and standard deviations
![]() of the rms errors
of the rms errors ![]() given by eq. (7).
These values have been extracted from trajectories of 0.4ps duration.
In addition, the values for the average energy drifts
given by eq. (7).
These values have been extracted from trajectories of 0.4ps duration.
In addition, the values for the average energy drifts ![]() as calculated from trajectories of
as calculated from trajectories of ![]() ps duration, are given.
ps duration, are given.
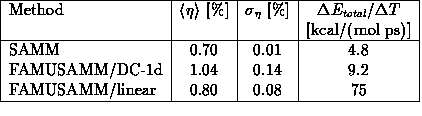
Table:
Approximation errors of force calculation for various methods as
measured by the time average ![]() of the
rms error, eq. (7), and by its standard deviation
of the
rms error, eq. (7), and by its standard deviation ![]() ;
also given are average energy drifts
;
also given are average energy drifts ![]() reflecting
algorithmic noise.
reflecting
algorithmic noise.
As can be seen,
the average rms errors ![]() of force
approximation are of about the same size (1%)
for all three methods.
The
of force
approximation are of about the same size (1%)
for all three methods.
The ![]() values of the FAMUSAMM algorithms
are only slightly larger than that of SAMM.
Thus, the multiple-time-step extrapolation procedures do not seem to
sizably reduce the quality of force approximation achieved
by SAMM.
In contrast, as shown in ref. [19], cutoff
methods exhibit errors
values of the FAMUSAMM algorithms
are only slightly larger than that of SAMM.
Thus, the multiple-time-step extrapolation procedures do not seem to
sizably reduce the quality of force approximation achieved
by SAMM.
In contrast, as shown in ref. [19], cutoff
methods exhibit errors ![]() which are larger
by at least a factor of ten.
Thus, as far as the quality of force approximation is concerned,
the FAMUSAMM procedures essentially preserve the
advantageous properties of SAMM.
which are larger
by at least a factor of ten.
Thus, as far as the quality of force approximation is concerned,
the FAMUSAMM procedures essentially preserve the
advantageous properties of SAMM.
But considering the fluctuations ![]() of the error
of the error
![]() , a distinct difference between
SAMM and the FAMUSAMM schemes becomes apparent.
Due to the application of the multiple-time-step extrapolation procedures,
for FAMUSAMM the fluctuations
, a distinct difference between
SAMM and the FAMUSAMM schemes becomes apparent.
Due to the application of the multiple-time-step extrapolation procedures,
for FAMUSAMM the fluctuations ![]() are
tenfold larger than for SAMM.
Thus the question arises, whether the slightly larger values of
are
tenfold larger than for SAMM.
Thus the question arises, whether the slightly larger values of
![]() and the drastically increased values of
and the drastically increased values of
![]() for the FAMUSAMM methods are accompanied
by comparable increases of algorithmic noise.
for the FAMUSAMM methods are accompanied
by comparable increases of algorithmic noise.
Consideration of the associated values for the energy
drifts in Table i reveals a slight increase for
FAMUSAMM/DC-1d as compared to SAMM which is in line with the corresponding
increase of ![]() . In contrast, a
dramatically enhanced algorithmic noise is apparent for the
FAMUSAMM/linear approach although in that case
. In contrast, a
dramatically enhanced algorithmic noise is apparent for the
FAMUSAMM/linear approach although in that case ![]() is nearly as small as for SAMM.
Hence, the superiority of the DC-1d scheme as compared to the linear
extrapolation
is actually preserved despite the
fact, that in FAMUSAMM extrapolations are applied to local Taylor expansion
coefficients representing approximated forces instead to explicitly
calculated exact forces.
Finally note, that the
is nearly as small as for SAMM.
Hence, the superiority of the DC-1d scheme as compared to the linear
extrapolation
is actually preserved despite the
fact, that in FAMUSAMM extrapolations are applied to local Taylor expansion
coefficients representing approximated forces instead to explicitly
calculated exact forces.
Finally note, that the ![]() values are uncorrelated to the
observed algorithmic noise; this finding underlines the validity of the
respective arguments presented in refs. [16]
and [20].
values are uncorrelated to the
observed algorithmic noise; this finding underlines the validity of the
respective arguments presented in refs. [16]
and [20].